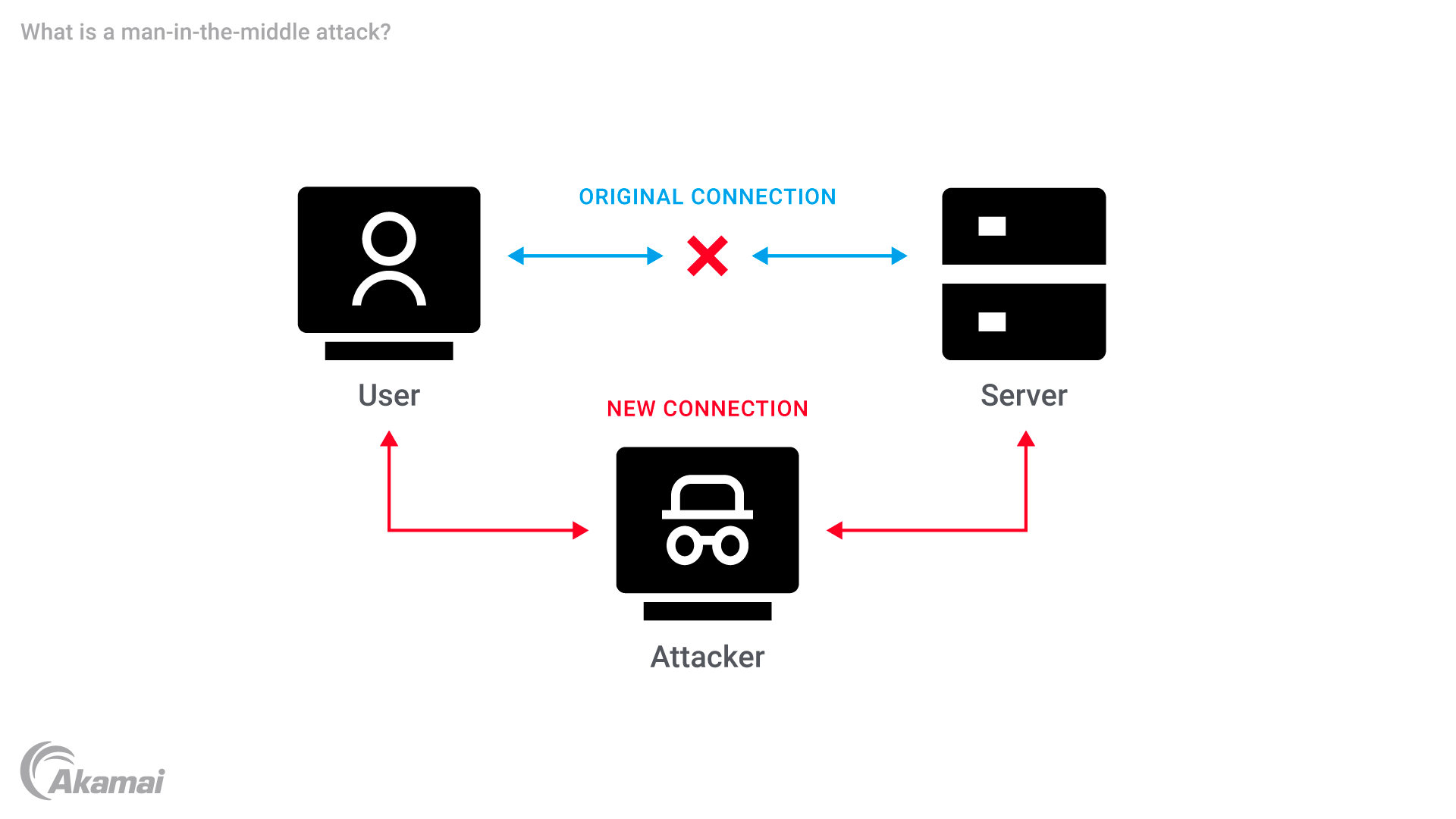
Man-in-the-middle attacks primarily rely on techniques like ARP spoofing, DNS spoofing, and session hijacking. These methods allow attackers to intercept and manipulate communications between two parties without detection, often leading to data theft or unauthorized access to systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, public Wi-Fi networks are a common target for MITM attacks because they typically lack encryption and do not require user authentication. Attackers can easily join the network and intercept unprotected data transmissions, making it essential to use VPNs or other encryption tools when accessing sensitive information on public Wi-Fi.
Common signs of a MITM attack include unexpected logout prompts, altered URLs leading to phishing sites, and suspicious certificate errors indicating potential tampering. In these attacks, a malicious hacker intercepts and manipulates communication between two parties, exploiting vulnerabilities to eavesdrop or modify data exchanges.
Users should remain vigilant for these signs to detect and mitigate potential MITM attacks, protect sensitive information, and uphold the integrity of their online interactions. Regular security awareness and updated anti-MITM measures are crucial for thwarting these malicious activities.
Tools effective in detecting a MITM attack include Wireshark, which analyzes network traffic for irregularities, and SSL/TLS scanners like SSL Labs, which identify vulnerabilities in cryptographic protocols. Additionally, a grey hat hacker can help alert organizations about potential security threats before a malicious actor takes action.
Encryption serves as a crucial defense against MITM attacks by rendering intercepted data unreadable to unauthorized entities. Through complex algorithms, encryption transforms data into ciphertext, making it virtually impossible for attackers to decipher without the corresponding decryption key.
In the context of MITM attacks, even if adversaries intercept the communication, they cannot make sense of the encrypted information without the proper credentials. This ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the exchanged data, forming a robust barrier against potential manipulation or eavesdropping. Regular security testing ensures encryption’s effectiveness, maintaining a solid defense against evolving MITM threats.
Your business may be at risk of a MITM attack if it operates on unsecured networks, lacks robust encryption measures, or neglects network monitoring. Unsecured networks provide opportunities for hackers to intercept and manipulate data exchanges, and the absence of encryption exposes sensitive information to potential eavesdropping.
Insufficient network monitoring makes it challenging to detect suspicious activities indicative of a MITM attack. Identifying and mitigating these risks is essential for your business to fortify its defenses, ensure a secure digital environment, and safeguard against potential threats to data integrity and confidentiality.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.