The benefits of network segmentation include improved cybersecurity by reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches, enhanced regulatory compliance, and better network performance by reducing congestion and optimizing traffic flows.
Network segmentation is a key cybersecurity practice that divides a computer network into smaller, isolated segments. This enhances network security by limiting the spread of threats and reducing the attack surface. By creating secure zones, organizations can better control access and monitor traffic, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Network segmentation is especially important in today’s complex, interconnected digital landscape. It helps reduce lateral movement, a common tactic hackers use to spread malware and deepen network access. Segmentation allows organizations to contain breaches and limit the damage of cyberattacks.
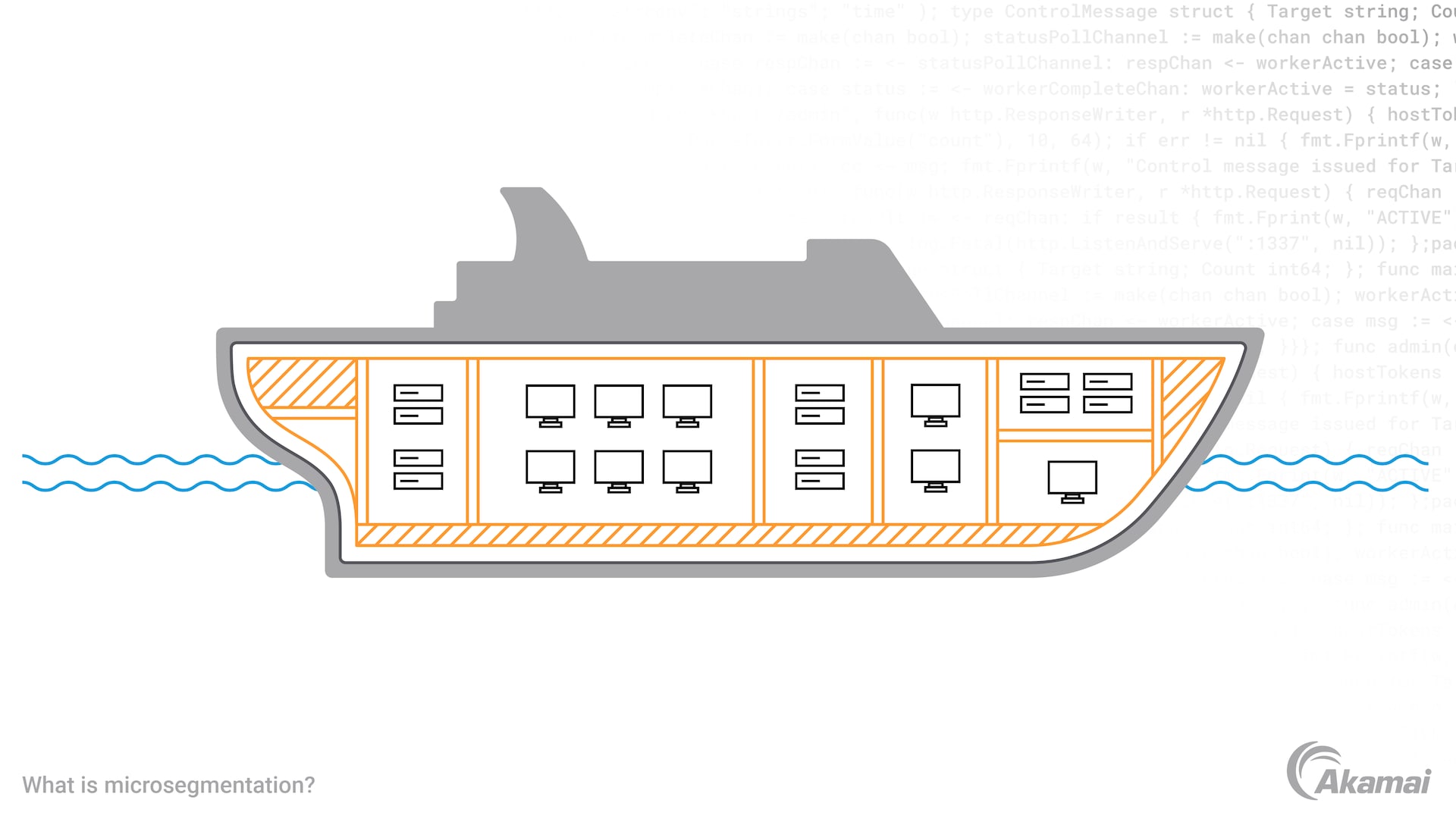
Just as compartmentalized sections in a ship help contain flooding from a hull breach, network segmentation can limit the spread of threats by isolating systems and data into secure zones.
Network segmentation isn’t only about security. It can also boost performance by reducing congestion and optimizing traffic flow. This is especially valuable for large enterprises with complex networks handling high volumes of data and transactions.
With the right segmentation policies, organizations can protect critical systems and sensitive data while maintaining overall network efficiency and reliability.
What are the benefits and applications of network segmentation?
Network segmentation offers a range of cybersecurity advantages. It reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches by limiting the attack surface and making lateral movement harder for attackers. If a breach occurs, segmentation helps contain the damage and prevent malware from spreading.
Segmentation also supports regulatory compliance. Standards like PCI DSS require strong controls to protect sensitive data. Isolating that data through segmentation helps meet compliance requirements and avoid fines or legal issues.
Improved network performance is another key benefit. By reducing congestion and optimizing traffic, segmentation enhances overall efficiency and reliability that are critical for high-availability, low-latency applications and services.
How does network segmentation strengthen security and performance?
Network segmentation is a foundational cybersecurity strategy that improves security controls, reduces vulnerabilities, and enhances network performance.
By creating secure zones, it limits lateral movement, reduces the attack surface, and helps prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. If a breach does occur, segmentation helps contain the impact and stop threats from spreading.
Segmentation also isolates critical systems and sensitive data important to satisfy regulatory compliance with standards like HIPAA and DORA. This approach enhances audit readiness and reduces legal and financial risk.
In addition to security, network segmentation boosts performance by reducing congestion and optimizing traffic flow. This improves efficiency and reliability, particularly for high-availability, low-latency applications and services.
As organizations adopt more cloud services and IoT devices, segmentation — together with Zero Trust principles discussed below — is becoming increasingly important in building secure, flexible, and resilient network architectures.
Network segmentation techniques: VLANs vs. subnets
Two common network segmentation techniques are VLANs (virtual local area networks) and subnets.
VLANs provide logical segmentation by creating multiple isolated broadcast domains within a single physical network, useful especially in large organizations where physical segmentation may be impractical or costly.
Subnets divide a network into smaller, physically separated segments. This can improve performance and security by limiting the number of devices on each segment, though it may introduce more complexity and management overhead.
Each method has its strengths. VLANs work well when logical separation is sufficient, while subnets are better for situations requiring physical isolation. Organizations should assess their specific needs to choose the approach that aligns best with their security and performance goals.
What are tools and devices for network segmentation?
Effective network segmentation relies on tools like firewalls, routers, and access control lists (ACLs). Firewalls enforce security policies by controlling traffic between segments, allowing or blocking it based on predefined rules.
Routers direct traffic between segments and the internet, and when equipped with advanced security features, they help strengthen network perimeters against external threats. ACLs define and enforce access policies, ensuring only authorized users and devices can reach specific resources.
Software-defined networking (SDN) and automation are also playing a growing role in network segmentation. SDN allows for flexible, dynamic network management, while automation reduces human error and consistent policy enforcement that can be valuable across cloud environments where configurations change frequently and quickly.
The role of microsegmentation and Zero Trust principles
Microsegmentation is an advanced form of network segmentation that creates secure zones around individual applications or devices. Unlike traditional segmentation — which uses broad, static boundaries — microsegmentation enables highly specific, dynamic security policies tailored to each resource.
This approach aligns closely with Zero Trust security principles that follow a “never trust, always verify” model. Zero Trust emphasizes least-privilege access, helping to ensure that users and devices access only the resources they need. Microsegmentation and Zero Trust, when combined, can strengthen an organization’s security posture, helping protect sensitive data and critical applications from sophisticated threats.
Microsegmentation is ideal for securing internal networks, managing IoT devices, and isolating sensitive systems.
For example, in healthcare instances, it can isolate patient records and medical devices, ensuring access is limited to authorized personnel. This not only enhances security but also supports regulatory compliance with standards like DORA, SWIFT, and SOC 2.
What’s the value of microsegmentation?
Microsegmentation gives organizations granular control over network traffic by enabling detailed security policies that monitor and restrict flows at the application or workload level. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. This is especially critical in cloud environments, where dynamic, flexible controls are essential.
Another major benefit is workload isolation. By segmenting different types of workloads into secure zones, organizations can protect critical applications and sensitive data from lateral threats. This is particularly important in data centers, where flat network architectures can expose systems to greater risk.
While microsegmentation may add some configuration and management overhead, the performance and security benefits are significant. It helps reduce congestion by optimizing traffic flows and ensuring only necessary data moves between segments, improving both reliability and resilience across the network.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Network segmentation is a cybersecurity practice that involves dividing a computer network into smaller, isolated segments to enhance security, limit the spread of cyberthreats, and reduce the attack surface.
Network segmentation improves security by limiting the spread of cyberthreats, reducing the attack surface, and making it more difficult for hackers to move laterally within the network. It also helps contain breaches and limit the damage caused by cyberattacks.
VLANs (virtual local area networks) are a form of logical segmentation that allows for the creation of multiple, isolated broadcast domains within a single physical network. They are useful in large organizations where physical segmentation may be impractical or too costly.
VLANs are logical segments that create isolated broadcast domains within a single physical network, while subnets involve dividing a network into smaller, physically separated segments. VLANs are ideal for logical segmentation, and subnets are better for physical separation.
Common tools and devices used for network segmentation include firewalls, routers, and access control lists (ACLs). Firewalls enforce security policies and control traffic flows, routers direct traffic between segments and the internet, and ACLs define and enforce access policies.
Network segmentation can improve network performance by reducing congestion and optimizing traffic flows. By isolating critical systems and sensitive data, it creates an environment where only necessary data is transmitted between segments, enhancing overall efficiency and reliability.
Network segmentation helps with regulatory compliance by ensuring that sensitive data is isolated and protected. Many industry standards, such as PCI DSS, require robust security controls, and segmentation can help organizations meet these requirements and avoid potential fines and legal issues.
Microsegmentation is a more granular form of network segmentation that focuses on creating highly specific and dynamic security policies. It allows for the creation of secure zones within the network, enhancing security and control over network traffic.
Microsegmentation is closely aligned with Zero Trust security principles, which advocate for a “never trust, always verify” mindset. By integrating microsegmentation with Zero Trust, organizations create an environment where users and devices only have access to the resources they need, enhancing overall security.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.

