Passkeys are a modern form of digital authentication that use biometric sensors (like Face ID or Touch ID) and public-key cryptography to provide a secure and user-friendly login experience. Unlike traditional passwords, which can be stolen or guessed, passkeys are stored locally on the user’s device and are never transmitted over the internet during authentication, making them more resistant to phishing attacks and data breaches.
Passkeys Explained
Passkeys are a big change in digital authentication. They are a safer and easier method to use than traditional passwords. These modern authentication methods leverage biometric sensors, such as Face ID and Touch ID, to provide a seamless and secure login experience. By eliminating the need for users to remember complex passwords, passkeys not only enhance security but also improve the overall user experience, making it easier and faster to access online accounts and services.
One of the key advantages of passkeys over traditional passwords is their resistance to phishing attacks and data breaches. Unlike passwords, which can be stolen through various means, passkeys are stored locally on the user’s device and are not transmitted over the internet during authentication. This means that even if a hacker manages to intercept the login process, they will not be able to access the user’s credentials. This robust security feature is particularly important in today’s digital landscape, where account takeover is a significant concern.
Passkeys are supported across a wide range of devices and platforms, including Apple, Android, and Microsoft devices. For instance, Apple’s implementation of passkeys through Face ID and Touch ID ensures that users can securely log into their accounts using biometric authentication. Similarly, Android devices and Microsoft’s Windows Hello offer comparable functionalities, making passkeys a versatile and widely accessible solution for enhancing online security.
Hardware passkeys
While software passkeys primarily rely on biometric sensors, hardware passkeys can offer an additional layer of security. These hardware devices are more resistant to malware than general purpose computers. Hardware passkeys are often used in conjunction with other authentication methods such as biometric sensors to create a multi-factor authentication (MFA) system that is highly resistant to attacks.
The primary difference between hardware passkeys and software passkeys is the method of key storage and generation. Hardware passkeys store the private key on a physical device, which must be present during the login process. In contrast, software passkeys use the user’s device itself to generate and store the key pairs, which makes them more convenient but also dependent on the security of that device. Both types of passkeys play a crucial role in enhancing the security of online accounts and services.
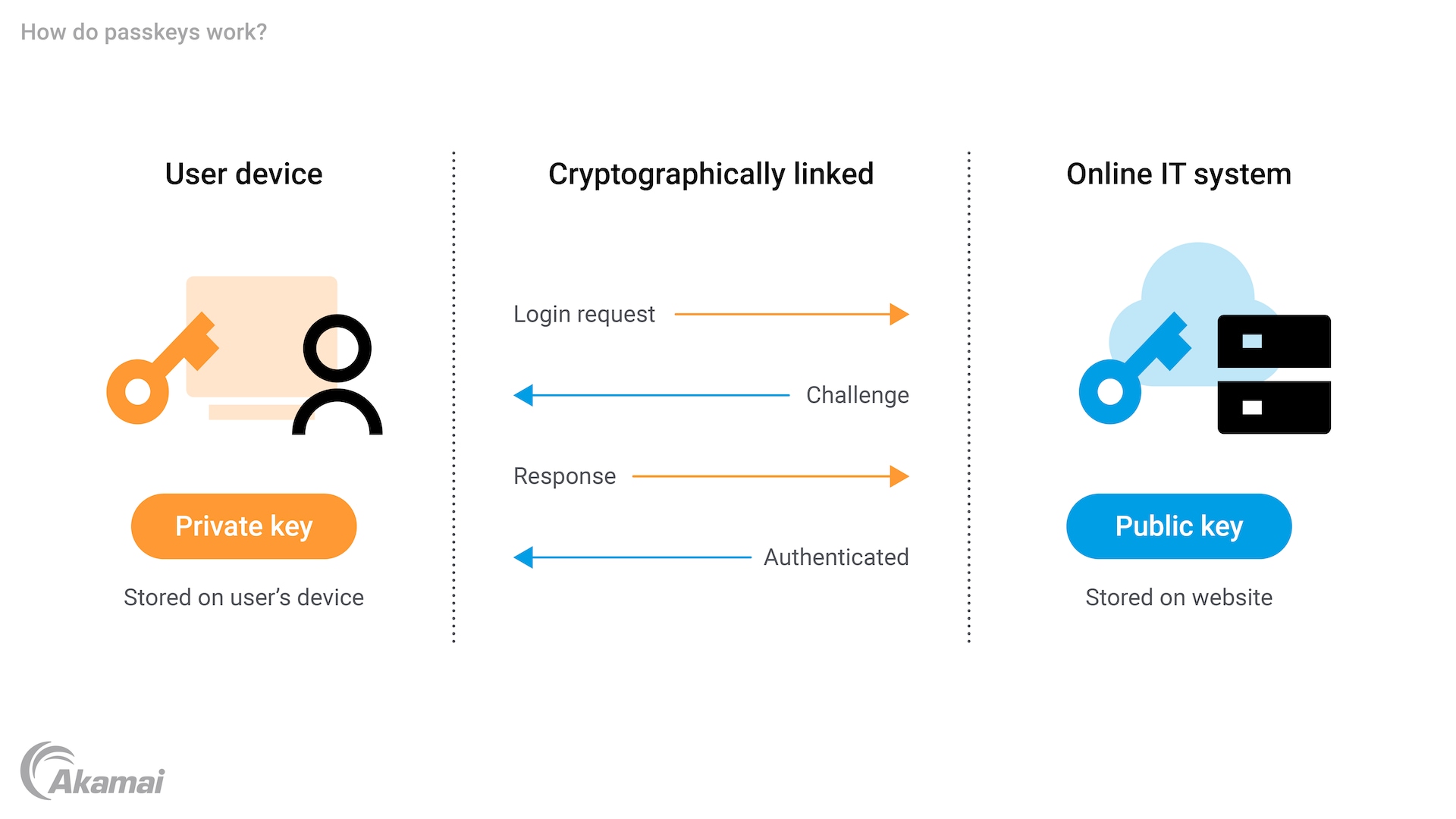
How do passkeys work?
The underlying technology behind passkeys is public-key cryptography, which involves the use of key pairs for secure authentication. When a user sets up a passkey, a unique key pair is generated on their device. The public key is shared with the service or website, and the private key remains securely stored on the user’s device. This ensures that the private key, which is essential for authentication, is never exposed to potential threats.
Web Authentication (WebAuthn) and FIDO2 standards are at the heart of passkey technology. WebAuthn is a web API that allows websites to interact with the user’s device to perform secure authentication. FIDO2 is a set of technical specifications that define how passkeys should be implemented and used. Together, these standards ensure that passkeys are compatible across different platforms and devices to provide a consistent and secure authentication experience.
Passkeys are supported by a variety of devices and platforms, including iOS, macOS, Windows Hello, and Android. Major browsers like Safari and Chrome also offer passkey support, which makes it easy for users to set up and use passkeys across their online accounts. The integration of passkey app, passkey API, and passkey manager further simplifies the process to allow users to manage their passkeys efficiently and securely.
Using passkeys
Setting up passkeys is a straightforward process that can be completed on mobile devices and other computing devices. For example, on an iPhone, users can set up a passkey using Face ID or Touch ID through the Safari browser or installed apps. Similarly, Android users can set up passkeys using their device’s biometric authentication factors. Once set up, passkeys are typically synced via password managers like iCloud Keychain or Google Password Manager to ensure that users can access their passkeys across multiple devices. Platform authenticators can also be used to generate credentials that are never synced to any remote service, giving organizations more control over how their passkeys are distributed.
The user experience with passkeys is significantly improved compared to traditional passwords. Passkeys offer a passwordless login option, which not only enhances security but also reduces the friction associated with entering and managing complex passwords. This seamless authentication process is particularly beneficial for users who frequently access multiple online accounts and services, as it eliminates the need to remember or store numerous passwords.
Many websites and services now support passkeys, including popular platforms like Google, Apple, and Microsoft. By adopting passkeys, these companies are taking a significant step toward a more secure and user-friendly authentication ecosystem. Users can benefit from enhanced security features, such as phishing-resistant login, while enjoying a smoother and more convenient login process. As more websites and services begin to support passkeys, the adoption of this technology is expected to grow, further reducing the risk of account takeover.
Comparing passkey authentication methods
Passkeys offer several advantages over traditional passwords, particularly in preventing account takeover. Unlike passwords, which can be easily compromised through phishing attacks or data breaches, passkeys are stored locally on the user’s device and are never transmitted over the internet during authentication. This makes them inherently more secure and less vulnerable to interception by hackers.
Passkey authentication can be seamlessly integrated with multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems, providing an additional layer of security. For example, a user who set up a passkey using their device’s biometric sensor may also be required to use a hardware passkey for certain high-security environments. This combination of factors makes it extremely difficult for unauthorized users to gain access to an account, even if they manage to bypass one layer of security.
While passkeys are designed to replace traditional passwords, users still have the flexibility to use passwords alongside passkeys for their accounts. This hybrid approach allows users to gradually transition to passkey authentication while maintaining the convenience of using passwords for services that do not yet support passkeys. However, the ultimate goal is to move toward a passwordless future, where the risk of account takeover is significantly reduced.
Passkey challenges and considerations
Despite their numerous advantages, passkeys are not without their challenges. One of the primary concerns is device compatibility. While major tech companies like Apple, Google, and Microsoft have implemented passkey support, not all devices and platforms are currently compatible. This can create barriers for users who wish to adopt passkeys but are limited by their existing technology.
Another consideration is the privacy of biometric data. Passkeys rely on biometric authentication, which involves the use of sensitive information like facial recognition and fingerprint data. While this data is stored locally on the user’s device and is not transmitted over the internet, there are concerns about how this data is protected and used. Users must trust that their biometric data will be handled securely and that it will not be misused by the device manufacturer or any third parties.
The adoption of passkeys across all platforms and services is also a challenge. While many major tech companies and websites have begun to support passkeys, there are still many legacy services and platforms that have not yet implemented this technology. This can create a fragmented user experience, where some accounts are secured with passkeys and others remain vulnerable to traditional password-based attacks. However, ongoing developments by the FIDO Alliance and tech giants like Google and Amazon are expected to drive broader adoption and standardization of passkeys.
Passkeys for enterprises
Passkeys are highly relevant to enterprises, as they offer a more secure and user-friendly alternative to traditional password-based authentication. By leveraging public-key cryptography and device-based authentication, passkeys provide phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication that can be seamlessly integrated into single sign-on (SSO) with existing identity provider (IdP) solutions. Enterprises can incorporate passkeys into their authentication workflows through various methods including WebAuthn, which is built into web browsers and FIDO2 SDKs for native applications.
Many MFA providers such as Akamai now support passkeys or similar passwordless technologies, making it possible for businesses to secure logins with passkeys through configuration rather than complicated custom development. Enterprises benefit from enhanced security, fewer support requests, and an improved user experience when passkeys are adopted. Passkeys can be deployed to specific user groups before gradually expanding to the rest of the organization, allowing time to invest in user education and compatibility across applications.
Future prospects
The future of passkey technology looks promising, with continuous advancements and support from leading tech companies. The FIDO Alliance, a nonprofit organization dedicated to reducing the world’s reliance on passwords, is actively working on improving passkey standards and promoting their adoption. Tech giants like Google and Amazon are also investing in passkey technology, recognizing its potential to enhance the security and user experience of their services.
As passkey technology matures, we can expect to see more widespread adoption across different devices and platforms. This will not only improve the security of online accounts but also make the login process more convenient and user-friendly. The integration of passkeys with existing password managers and authentication systems will further simplify the transition to a passwordless future, where the risk of account takeover is minimized.
The journey to a fully passkey-secured ecosystem is not without its hurdles. Addressing issues related to device compatibility and biometric data privacy will be crucial in gaining user trust and ensuring widespread adoption. Educating users about the benefits and proper use of passkeys is an essential step toward making this technology a mainstream authentication method. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of passkeys make them a compelling choice for enhancing the security of online accounts and services.
Passkeys represent a significant advancement in digital authentication, offering a more secure and user-friendly alternative to traditional passwords. By leveraging biometric sensors and public-key cryptography, passkeys provide a robust defense against phishing attacks and data breaches. As more devices and platforms adopt this technology, the future of online security looks brighter, with a reduced risk of account takeover and a smoother user experience. For more information on passkeys and how they can enhance your online security, read Akamai’s latest blog posts on modern authentication methods.
Frequently Asked Questions
Passkeys enhance online security by eliminating the need for users to remember passwords, which are often weak and easily guessed. Storing private keys locally on the user’s device prevents hackers from obtaining the user’s authentication credentials. Passkeys also support multi-factor authentication (MFA), adding an extra layer of security to the login process.
Passkeys use public-key cryptography, which involves generating a unique key pair on the user’s device. The public key is shared with the service or website, and the private key remains securely stored on the user’s device. WebAuthn and FIDO2 standards ensure that passkeys are compatible across different platforms and devices.
Setting up a passkey is straightforward and can be done through your device’s operating system or web browser. For example, on an iPhone, you can set up a passkey using Face ID or Touch ID through the Safari browser. Similarly, Android users can set up passkeys using their device’s biometric authentication factors.
Yes, passkeys can be synced across multiple devices using password managers like iCloud Keychain or Google Password Manager. This allows you to access your passkeys on different devices, ensuring a seamless and secure login experience. Platform authenticators can also be used to generate credentials that are never synced to any remote service, giving you more control over how your passkeys are distributed.
No, hardware passkeys and software passkeys differ in how they store and generate keys. Hardware passkeys are physical devices that store the private key and must be present during the login process. Software passkeys are created and stored on the user’s computer or mobile device, which makes them more convenient but also dependent on the security of that device.
The main benefits of using passkeys include enhanced security, resistance to phishing attacks, and a more user-friendly login experience. Passkeys reduce the risk of account takeover and make it easier for users to access their online accounts without the need to remember or manage complex passwords.
Yes, you can still use passwords alongside passkeys. This hybrid approach allows you to gradually transition to passkey authentication while maintaining the convenience of using passwords for services that do not yet support passkeys. However, the ultimate goal is to move toward a passwordless future for enhanced security.
Some challenges associated with passkey adoption include device compatibility, concerns about the privacy of biometric data, and the need for broader support across platforms and services. Not all devices and platforms currently support passkeys, and users must trust that their biometric data is handled securely.
Biometric data used for passkeys is stored locally on your device and is not transmitted over the internet. To ensure privacy, it’s important to use devices from trusted manufacturers and to keep your device’s software up to date. Additionally, understanding the privacy policies of the device manufacturer can help you make informed decisions about using passkeys.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.