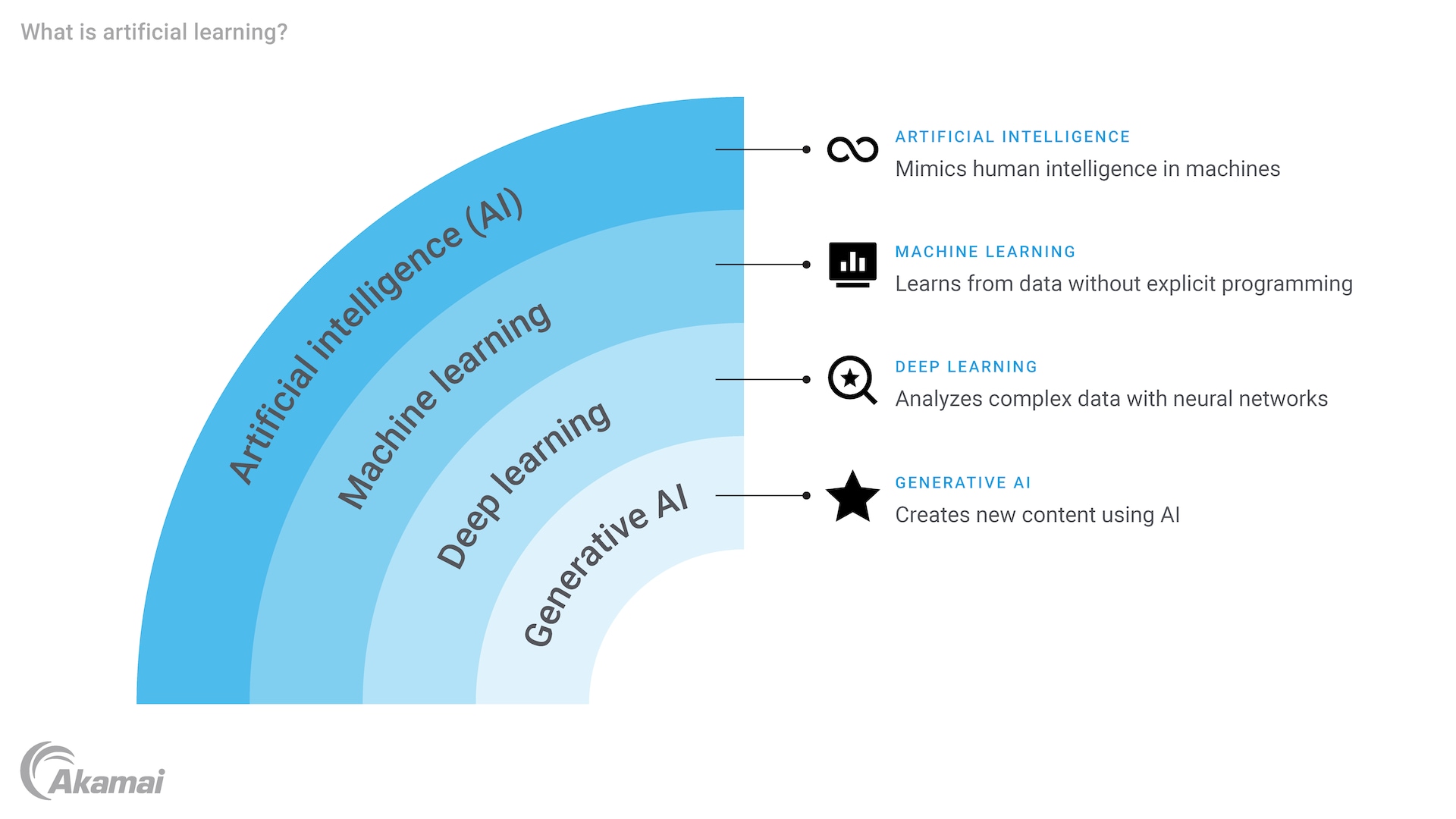
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science that focuses on creating machines and systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as problem-solving, decision-making, learning, and understanding language. AI encompasses technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, enabling applications like virtual AI assistants, autonomous vehicles, and advanced data analytics. It aims to mimic human cognitive processes to make systems smarter and more efficient.
Frequently Asked Questions
Artificial learning is the process by which machines or computer systems mimic human intelligence by analyzing data, identifying patterns, and improving their performance over time. It encompasses a broad range of techniques, including machine learning, neural networks, and deep learning, allowing systems to adapt and evolve in tasks like decision-making, problem-solving, and prediction. Artificial learning powers intelligent systems such as recommendation engines, robotics, and generative AI models.
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that enables computers to learn from datasets without being explicitly programmed. ML uses algorithms to identify patterns, make predictions, and adapt as new data becomes available. Common applications include fraud detection, personalized recommendations, and predictive analytics in fields like healthcare and finance.
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses multilayered neural networks to analyze complex data and learn hierarchical patterns. These networks, often called deep neural networks, excel in processing unstructured data like text, images, and audio. Deep learning powers advanced AI applications such as computer vision, speech recognition, and generative AI, making it highly effective for tasks requiring accuracy and scalability.
A neural network is a type of machine learning model inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, consisting of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons). Neural networks process data through these layers, identifying patterns and relationships to make predictions or classifications. They are fundamental to deep learning and are widely used in applications like image recognition, language translation, and recommendation systems.
Generative AI refers to AI systems that create new content, such as text, images, music, or videos, based on input data. These systems use generative models, like GANs (generative adversarial networks) or large language models such as ChatGPT, to produce outputs that are often indistinguishable from human-generated content. Generative AI is widely used in creative industries, content automation, and virtual environments.
A large language model (LLM) is a type of AI system trained on massive amounts of text data to understand and generate human-like language. LLMs, such as GPT and BERT, leverage deep learning techniques to perform tasks like text completion, summarization, translation, and conversational AI. They are widely used in chatbots, virtual assistants, and tools that require advanced language understanding.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.