©2025 Akamai Technologies
Contents
What Is CI/CD?
CI/CD stands for continuous integration/continuous deployment. It’s a software development practice that involves automating the process of integrating code changes from multiple developers into a shared repository, testing those changes, and deploying them to production environments. By automating the software release process, CI/CD aims to improve collaboration, increase productivity, and reduce the time it takes to deliver new features or bug fixes to end users.
The practice of continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) of software code is an area of the technology trade that people tend to discuss without completely understanding. Most of us have a general sense of what CI/CD is about, but if you are an actual stakeholder in software development, it pays to get the details right. That’s the purpose of this article.
One reason that CI/CD can be confusing is that it’s at once an idea, a set of practices and processes, and a sprawling toolset. It’s related to, but different from, DevOps and agile software development methodologies. Doing DevOps and agile doesn’t mean you are automatically doing CI/CD.
The purpose of CI/CD is to make software development organizations work more quickly and precisely — rolling out features that users want at a rapid pace. CI/CD crucially allows software experiments with fast feedback loops. At its root, CI/CD is a coding philosophy. The goal is to integrate new, small code changes into applications as they become available and then deliver them into production on a continuous basis. This combination of continuous integration and continuous delivery forms a cycle that enables rapid feedback and deployment with minimal effort. Making this work requires solutions and processes, but those are simply the means of implementing the underlying concept.
What is continuous integration (CI)?
To understand CI, and CI/CD in general, it’s worth taking a moment to review earlier software integration practices. The process of integration involves developers “checking in” new code they have written into a central version repository. This process typically involves developers pushing code to a shared source code repository managed by version control systems such as Git, which enables efficient collaboration and version management. From there, the new code is integrated into the overall code base of the application.
This was, and still is, a manual, intermittent process in many cases. In the “waterfall” approach to software development, integration may occur once every six months. There’s nothing wrong with this mode of integration. It’s just slow and not well suited to a development strategy that calls for frequent feature updates.
With CI, development teams frequently implement small code changes, using automated processes to build, package, and test applications. When developers push code to the shared repository, CI tools can automatically perform static code analysis and code review to identify bugs, quality issues, and integration problems early in the pipeline. Working this way, developers can commit to code changes frequently, resulting (hopefully) in better code quality and collaboration between Dev, Ops, and QA teams. This isn’t a simple matter, given that the code often comes from different platforms. CI provides a consistent mechanism for integrating and validating code changes.
What is continuous delivery (CD)?
CD is about putting the newly integrated code into production. CI comes first, followed by CD, which pushes the validated code out onto the infrastructure that hosts the application. Often, CD delivers the code to a testing platform before it is released for end users. CD is an automated process that takes care of updating the various databases and web servers and other systems that must be changed or restarted once the new version of the application is deployed.
Like CI, CD is an automated, faster-paced version of an older practice. Code delivery was, and still is in many cases, a labor-intensive process. CD leverages specialized tooling to enable code delivery on a continuous basis, sometimes as often as every hour. The operations team plays a crucial role in deploying code releases to production environments, ensuring smooth and reliable transitions of validated code to live systems.
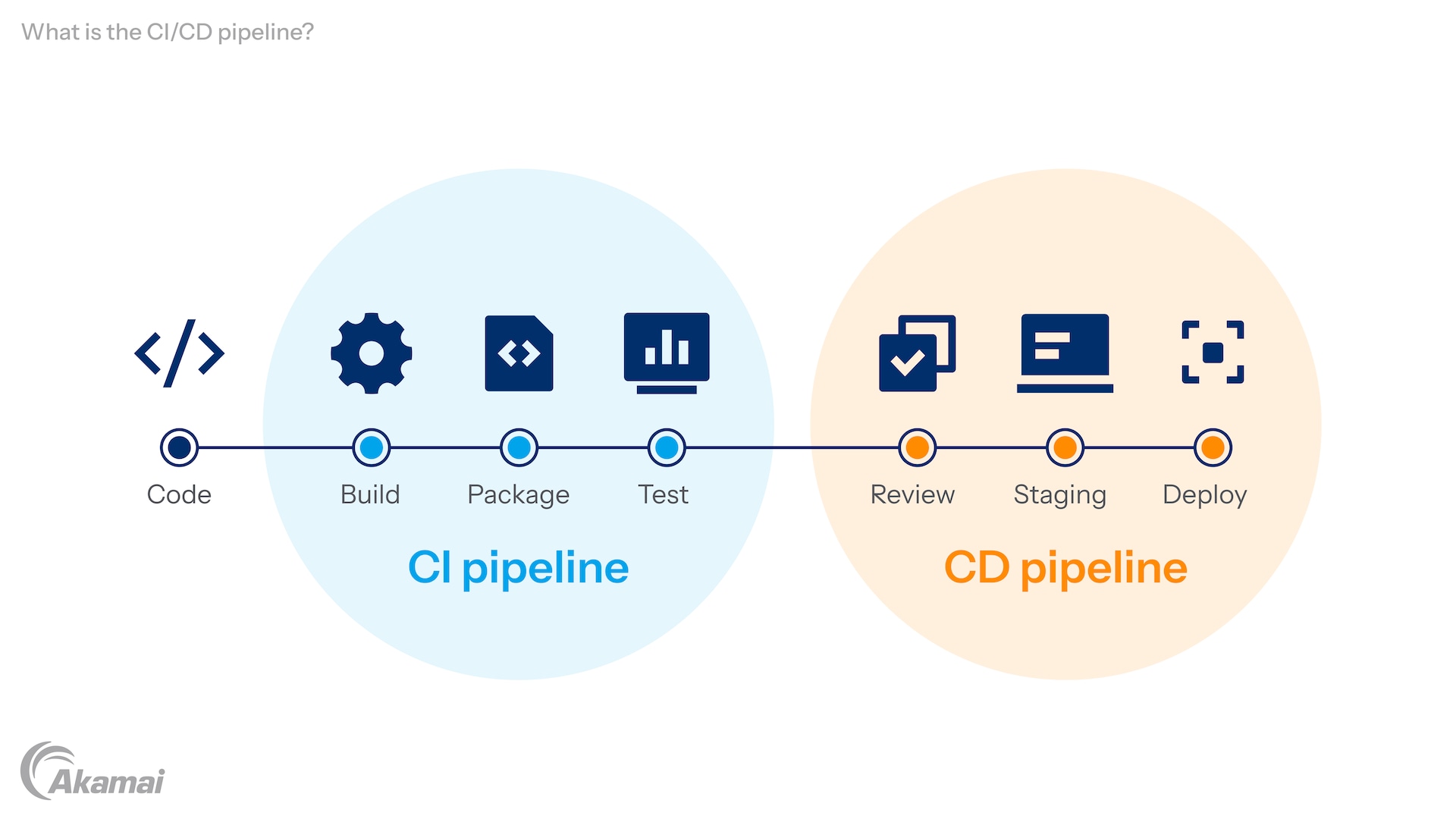
What is the CI/CD pipeline?
The CI/CD process comprises multiple stages: build, package, test, and deploy. The flow from one stage to the next creates something resembling an assembly line of new code components working their way toward deployment. This is known as the CI/CD pipeline. There may be dozens of code components going through the pipeline, grouped by stage. At each stage, code is automatically tested using test scripts stored alongside the code in version control repositories. These test scripts are used for integration testing and regression tests to ensure that new changes don’t break existing functionality and that different modules work together as expected. CI/CD pipelines work using automation software that executes builds, performs quality control tests, and then pushes the builds out to their proper production environments.
Benefits of CI/CD pipeline
The CI/CD pipeline offers a range of benefits to a software-producing organization. The automation inherent in the pipeline speeds up the delivery of code, allowing teams to gather user feedback more quickly and iterate on improvements. Reducing the length of the delivery process usually translates into faster time to market for new features.
Done right, an automated CI/CD pipeline should also improve software quality. The pipeline produces a continuous feedback loop from quality stakeholders. Testing is more thorough and occurs earlier in the software lifecycle — the so-called “shift left” phenomenon. Defects and code failures get detected and fixed early, before they can go into production and cause user experience problems and costly remediation projects. Overall, the greater speed and efficiency of the CI/CD pipeline almost always translates into reduced costs.
Source code management and CI/CD
Managing source code effectively is essential to a successful CI/CD pipeline. A well-structured code repository, such as one hosted on Git, enables developers to collaborate efficiently and maintain a clean, version-controlled codebase. CI/CD starts when developers push their changes to the repository. Once code is committed, automated build processes can trigger unit tests to ensure the new changes integrate smoothly without breaking existing functionality.
Incorporating unit tests early in the development lifecycle minimizes the likelihood of errors, ensuring that the software delivery pipeline remains stable. The automated testing mechanisms integrated within a CI/CD pipeline provide immediate feedback, allowing developers to identify and resolve issues early. Effective source code management also ensures a seamless transition through the pipeline’s stages, from testing in the development environment to final deployment.
A well-organized code repository is the foundation of a reliable CI/CD process, fostering collaboration and maintaining software quality. This streamlined approach reduces manual tasks and expedites code deployment, allowing for continuous updates without disruptions.
Continuous delivery pipeline for Kubernetes
For modern cloud-based applications, particularly those running on Kubernetes, the CD workflow plays a crucial role in achieving scalability and agility. Kubernetes provides an ideal environment for managing containerized applications, allowing CI/CD pipelines to deploy updates seamlessly. After the source code passes all testing phases, the CD pipeline can trigger automated deployments to a Kubernetes cluster, making the updates immediately available in the development environment or production.
The deployment process includes tasks like updating compute instances on Akamai Cloud or configuring new containers within Kubernetes pods. With the help of automation tools, changes can be deployed continuously without downtime, ensuring that web applications remain accessible even during updates. This approach not only ensures the smooth rollout of new features but also allows for real-time scalability to handle fluctuating workloads.
The power of Kubernetes in CI/CD lies in its ability to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Coupled with a robust CI/CD pipeline, Kubernetes enhances the speed and efficiency of the software delivery process, optimizing both development and operational teams.
How does CI/CD relate to DevOps?
CI/CD is different from DevOps. The two processes can work independently of one another. Yet they are made for each other. DevOps is the fusion of software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops). It unifies the previously separate processes, and respective teams, for developing and releasing software. CI/CD is a natural fit for DevOps as a result. The common DevOps and CI/CD toolsets work together, making CI/CD a key component of modern DevOps practices by providing the automation and collaboration necessary for effective software delivery. For example, CD tools usually have a dashboard that shows DevOps teams if a build fails, and so forth. In some cases, it’s the same toolset, with DevOps and CI/CD functionality built in.
API security testing within CI/CD
It’s a little odd that there’s no “T” in the terms CI/CD and DevOps. CI/CD should really be CI/CT/CD, including the very important continuous testing that goes on in the process. DevOps should be DevTestOps, but that would be a mouthful.
Automated testing is a critically important part of CI/CD. Tests vary by team, but the testing regimen usually includes static and dynamic testing of the code, along with security tests like software composition analysis (SCA), which looks for vulnerable code in open source components. Increasingly, automated testing in CI/CD also incorporates the testing of application programming interfaces (APIs). This practice is necessary today because so many apps, especially those that are cloud native, make extensive use of API calls to other pieces of software. APIs are essentially software programs themselves, so they should be naturally incorporated into the pipeline flow.
Since APIs expand the attack surface, it is essential to test them for security gaps. They can allow a malicious actor to directly access data protected by the API, for instance. For this reason, it is a good practice to run tests on APIs that look for defects in API user authentication and configuration errors, along with, but not limited to, the OWASP API Security Top 10 list of API risks.
CI/CD is an essential element of software development today. It speeds up the deployment of new code, which is useful for businesses that base their competitive advantage on great user experiences. Not only can they get new features to end users more quickly, but they can also save money by working smarter and faster at the same time. CI/CD functions like a pipeline, with new code moving through the build-package-test-deliver workflow in an automated process. Security testing, including API security, is a best practice, given the interconnected nature of modern software.
Frequently Asked Questions
There are several best practices to follow when implementing CI/CD in your organization, including:
- Automate processes to minimize errors and expedite delivery.
- Write comprehensive automated tests covering unit, integration, and end-to-end testing.
- Utilize version control for organized repository management.
- Implement Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for consistent environments.
- Monitor key metrics for performance evaluation and improvement.
Some of the main challenges of implementing CI/CD include:
- Cultural resistance to change: To help overcome this challenge, foster a healthy culture of collaboration and communication by providing training, workshops, and demonstrations of CI/CD benefits via success stories.
- Integration issues with legacy systems: Try to gradually update outdated systems to make them compatible with CI/CD, implementing adapter layers or APIs to bridge the gap.
- Ensuring proper test coverage: Prioritize automated testing and regularly review test coverage. Consider using tools to help identify areas with low test coverage.
- Managing infrastructure and configuration changes: Implement infrastructure as code (IaC). Utilize containerization for consistent application deployment.
- Balancing speed with stability in the deployment process: Try implementing gradual deployment strategies like canary releases or blue-green deployments. Also, use toggles to selectively enable or disable features as needed. Establish a rollback plan, just in case.
CI/CD can positively impact security in software development. Automated security checks catch vulnerabilities quickly, continuous monitoring provides real-time security insights, and the DevSecOps culture fosters collaboration between development, operations, and security teams, which eventually helps address concerns early in the development lifecycle.
Kubernetes plays a crucial role in automating the deployment and scaling of containerized applications in a CI/CD pipeline. Once code changes are tested and validated, they can be deployed seamlessly into Kubernetes clusters, which manage the containers automatically. This allows for real-time scaling and smooth updates, enabling continuous delivery of applications in cloud native environments.
Unit tests are vital in ensuring that code changes do not introduce errors. As part of the CI process, unit tests validate individual components of the codebase. If any test fails, the CI/CD pipeline halts, allowing developers to address issues before moving to the next stage. Automated testing ensures that only high-quality code advances through the delivery pipeline, improving overall software reliability.
Implementing CI/CD for legacy systems can be challenging due to older, monolithic architectures that may not support modern development practices like containerization or Kubernetes. Integration issues, lack of automated testing, and limited tooling support are common hurdles. Organizations must often refactor or modularize their legacy systems, and gradually introduce CI/CD principles to improve efficiency and scalability.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.