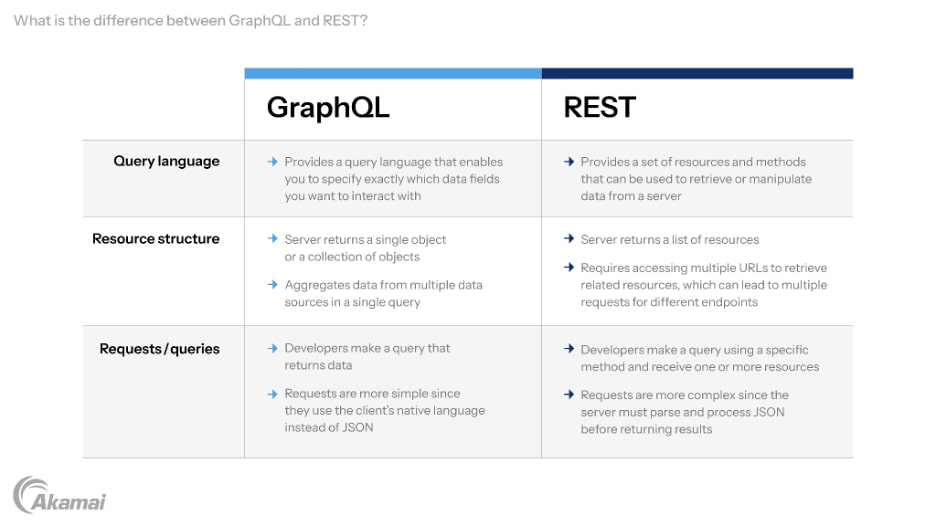
GraphQL is a query language and runtime for APIs (application programming interfaces) that was developed by Facebook. It provides a more efficient and flexible way to request and manipulate data from servers compared to traditional RESTful APIs. Unlike typical REST APIs, which require multiple URLs for different resources, GraphQL operates through a single endpoint (or one endpoint), simplifying data access. With GraphQL, clients can specify the exact data they need, avoiding over-fetching or under-fetching of information.
GraphQL is a query language for APIs. It was developed by Facebook engineers in 2012 and has since gained popularity among developers working on large-scale web applications. Positioned as a more robust alternative to traditional RESTful APIs, GraphQL is built on the principles of graph theory, which is a set of mathematical concepts that describe how networks of objects (nodes) interact with each other.
With GraphQL, querying APIs is simplified through the use of precise and concise requests. Just like how you would communicate with a friend about dinner plans or weekend activities, you can describe your needs to the API using variables and filters, making sure that you receive the exact desired response. Notable implementations of GraphQL include Facebook’s GraphQL, GitHub’s GraphQL API, Salesforce’s App Cloud Connect service, and other global adopters.