Endpoint protection enhances network security by providing comprehensive security measures that protect endpoints, such as desktops, laptops, servers, and IoT devices, from various cyberthreats. Endpoint security solutions integrate antivirus software, firewalls, EDR, DLP, and encryption to safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Common Types of Endpoint Security Explained
Endpoint security plays a vital role in safeguarding individual users’ personal devices (from security threats like phishing, malicious downloads, and intrusion) as well as organizational assets (from advanced persistent threats, data breaches, and intellectual property theft). In this article, we cover the common methods that organizations pursue to secure their endpoints.
Endpoint security is a vital component of cybersecurity that focuses on protecting endpoints such as computers, laptops, servers, and mobile devices within a network. These endpoints serve as entry points for potential cyberthreats and are often targeted by hackers seeking unauthorized access or sensitive data.
Endpoint security entails implementing a combination of hardware and software solutions to protect these endpoints from various attacks. The aim is to make sure that each endpoint device is shielded with security policies and stays shielded from malware infections, data breaches, unauthorized access attempts, and other cyberthreats. The importance of endpoint security has only increased with the popularity of remote work.
What is an endpoint?
An endpoint is a device or node that can both send and receive communications on a network. Common examples of endpoints include computers, laptops, servers, mobile phones, tablets, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, as well as any other device connected to a network.
Endpoints act as the primary means for users to reach network resources or connect with other endpoints within the network. They often communicate with applications and services on the server side to carry out various tasks such as retrieving files, sending and receiving emails, navigating websites, and transferring data between systems.
Every endpoint is assigned a unique identifier, called an IP address, which facilitates communication between various endpoints on the internet or local networks. These IP addresses allow endpoints to make information or service requests and receive replies from other devices within the network.
In addition to physical devices, endpoints can also include virtual machines or containers that operate on servers. These endpoints enable users, defined processes, automated scripts, software applications, and third-party services to communicate with the underlying infrastructure, including the network, server, and storage.
While endpoints facilitate connectivity, resource sharing, and collaboration, they also present significant security risks. Cybercriminals target these endpoints to gain unauthorized entry, disrupt their operations with malicious software, exploit weaknesses in software, and steal sensitive information. Therefore, it is crucial to establish adequate endpoint security measures, such as antivirus programs, personal firewalls, VPNs, and encryption protocols, to safeguard endpoints from potential dangers.
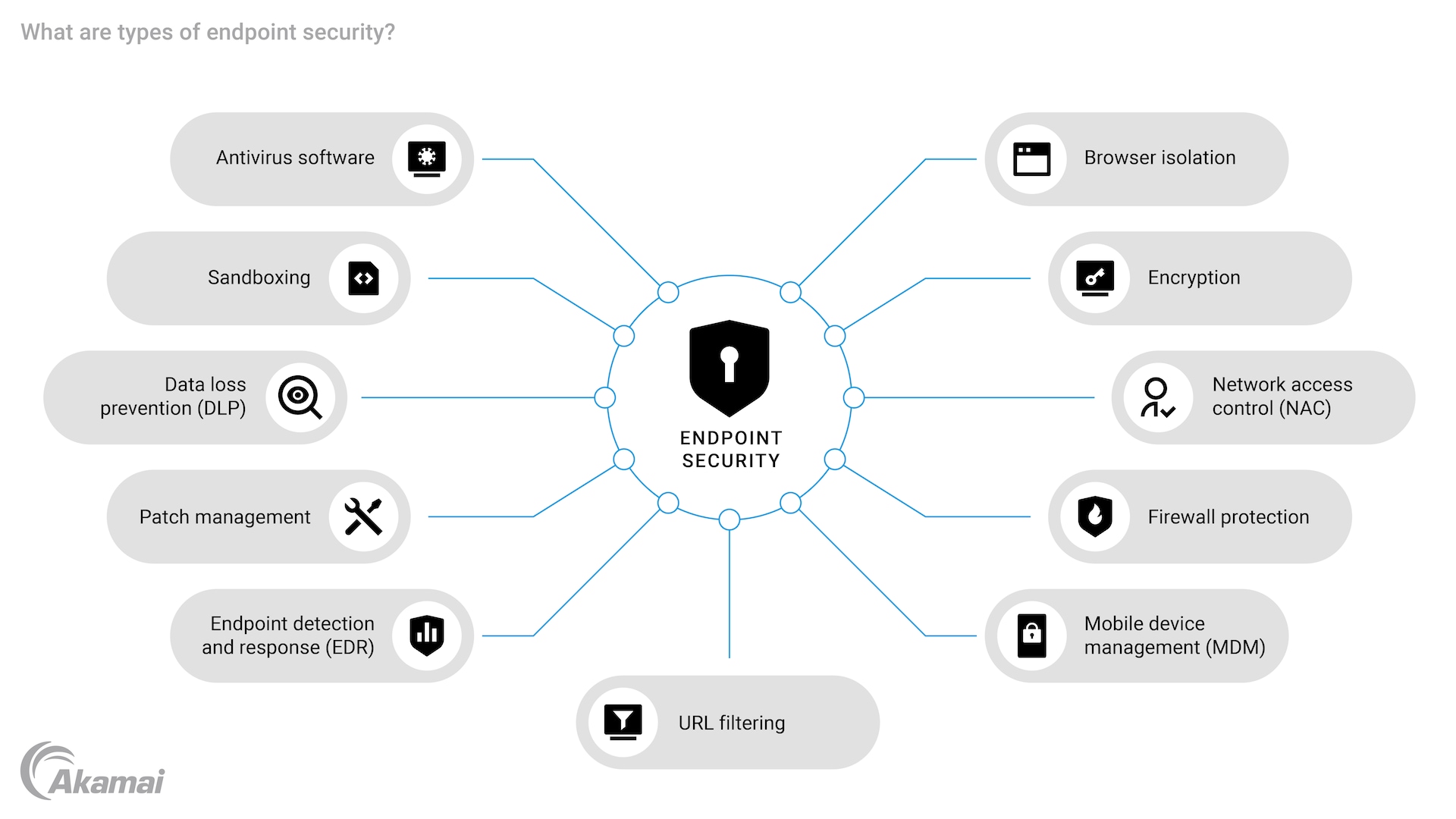
Types of endpoint security
These are some common types of endpoint security techniques that organizations use to safeguard their networks:
- Antivirus software: Antivirus software is a fundamental and indispensable component of endpoint security. It efficiently detects and removes malicious software, including viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, ransomware, adware, and other malware that pose a potential threat to the system.
- Firewall protection: A firewall serves as a protective barrier between internal trusted networks and external untrusted networks, such as the internet. Its primary function is to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined rules and policies. By doing so, firewalls act as guardians, diligently filtering out suspicious or malicious traffic to prevent unauthorized access attempts.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR): EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection capabilities by collecting real-time data from endpoints across the network. They monitor for unusual behavior patterns that indicate cyberattacks or breaches. EDR tools offer proactive detection and response mechanisms to swiftly mitigate potential threats before they cause substantial damage.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): Data loss prevention systems safeguard sensitive data by recognizing and blocking its unauthorized transmission outside of an organization’s controlled environment. DLP systems can identify patterns in communication to thwart attempts to leak confidential information. These systems monitor various channels such as email attachments, USB drives, and other data transfer methods.
- Patch management: Regularly updating software applications with patches helps fix vulnerabilities identified by developers or security researchers after their release. This is a critical preventive measure against potential attacks that exploit known vulnerabilities.
- Encryption: By encrypting data, we can make sure that even if it’s intercepted during transmission or while in storage (for example, through methods like SSL certificates or VPNs), it will remain unreadable without the appropriate decryption keys.
- Network access control (NAC): Network access control enforces security policies by controlling network access based on user identity, device type, and compliance status. Before granting access, NAC verifies the security posture of devices and makes sure that only authorized users with compliant devices are allowed entry.
- Mobile device management (MDM): As mobile devices become more prevalent in the workplace, mobile device management solutions have emerged as a crucial tool for enforcing endpoint security policies on smartphones and tablets. These solutions empower organizations to effectively manage, secure, monitor, and control mobile endpoints within their network infrastructure.
- Sandboxing: Sandboxes are virtual environments that mimic the functionality and behavior of an operating system or software application. They provide a safe and controlled space for untrusted programs or files to be run, making sure that they cannot access any resources or cause any harm outside the sandbox’s boundaries.
- Browser isolation: Browser isolation is a cybersecurity technique that protects users and their devices from web-based threats. It does this by creating an isolated environment for web browsing activities. Browser isolation separates the user’s browsing session from their local device and network by running it in a secure container or virtual machine.
- URL filtering: When a user tries to visit a website, the URL filter checks the requested URL against the set policy rules. If the website belongs to an allowed category based on the policy configuration, the user is granted access. On the other hand, if it matches any blocked category, the request is denied, and appropriate action is taken, such as displaying a block page or redirecting users to an alternative site.
API gateways in endpoint security
API gateways play a crucial role in securing endpoints by acting as intermediaries that manage and control API traffic between clients and servers. They enforce security policies, authenticate requests, and protect against threats such as DDoS attacks. By integrating API gateways with endpoint security solutions, organizations can enhance their network security and ensure that all endpoints communicating through APIs are secure.
API gateways also provide features such as rate limiting, encryption, and validation of HTTP requests, ensuring that endpoints are protected from malicious activities and unauthorized access attempts.
Endpoint protection and security solutions
Endpoint protection encompasses a range of endpoint security solutions designed to protect desktops, laptops, servers, and IoT devices from cyberattacks. These solutions include antivirus software, firewalls, EDR, DLP, and MDM systems. Endpoint security solutions provide comprehensive protection by integrating multiple security measures, such as application control, encryption, and network security protocols, to safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
By implementing robust endpoint protection, organizations can secure their network infrastructure, reduce the attack surface, and prevent potential breaches that could lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
API gateways are important for endpoint security because they manage and control API traffic between clients and servers, enforce security policies, and protect against threats like DDoS attacks. By integrating API gateways with endpoint security solutions, organizations can enhance their network security and ensure secure communication between endpoints.
Encryption plays a crucial role in endpoint security by ensuring that data remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption keys, even if intercepted during transmission or while in storage. This protects sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Mobile device management (MDM) solutions contribute to endpoint security by enforcing security policies on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. MDM allows organizations to manage, monitor, and secure mobile endpoints within their network, ensuring compliance with security standards and protecting against cyberthreats.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.