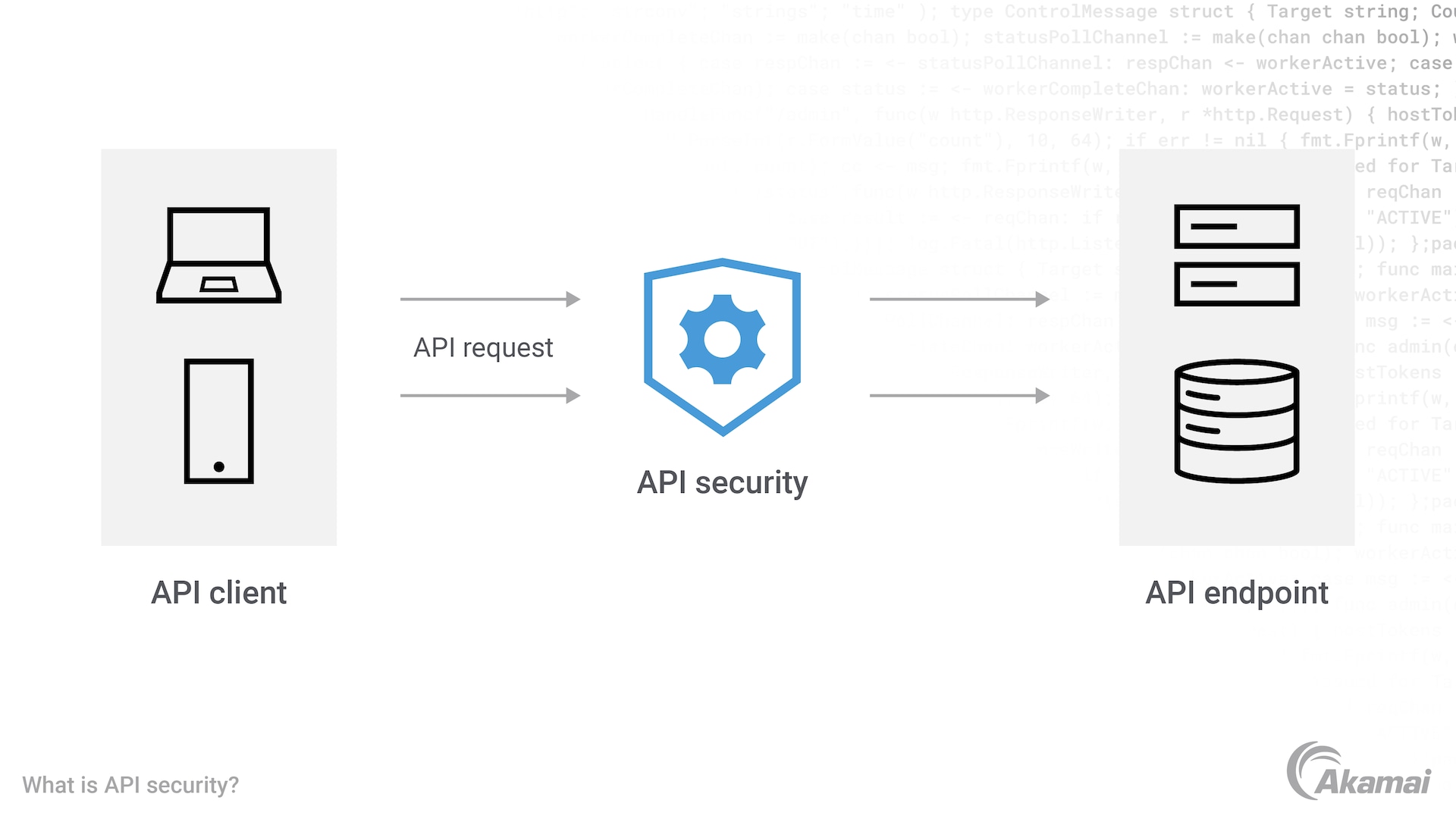
Agent-based API security involves deploying intelligent software agents directly into the API runtime environment. These agents monitor API traffic, detect vulnerabilities, and enforce security policies in real time. The agents analyze each API call and determine if it meets security standards before allowing data to be exchanged, providing an additional layer of protection against cyberattacks.
Agent-based API security involves the implementation of intelligent agents that act as intermediaries between clients and servers. These agents have a deep understanding of the requests being made to the API and can enforce security policies in real time.
One method of protecting APIs is through agent-based API security, which involves using intelligent agents to monitor and control the security of API interactions. These agents act as intermediaries between clients and servers, making sure that only authorized entities can access the API resources.
Agent-based API security is known for its capacity to offer precise access control. The agents possess a thorough comprehension of the API requests and can implement diverse security measures depending on elements like user identities, roles, authorizations, and even situational details. Through analyzing each request instantly, these agents can make informed choices on whether to grant or restrict access to specific resources.
Moreover, agent-based API security allows for early identification and prevention of potential threats. By constantly monitoring incoming requests, agents are able to detect any abnormal patterns or actions that may indicate a possible attack or breach. They can use machine learning techniques or predetermined rules to identify malicious behavior and respond accordingly, such as blocking specific IP addresses or requiring extra authentication measures.
Another benefit of agent-based API security is its ability to safeguard data through encryption methods, in addition to controlling access and detecting threats. The agents are able to encrypt sensitive information transmitted between clients and servers, utilizing commonly used encryption protocols such as TLS/SSL. This guarantees that if the data is intercepted by unauthorized parties, it cannot be deciphered without the correct decryption keys.
Overall, agent-based API security offers a robust framework that shields APIs from unauthorized access, malicious activities, and data breaches. It provides fine-grained control over access permissions, and actively detects and thwarts potential threats in real time. By using intelligent agents as intermediaries between clients and servers, organizations can effectively bolster their overall API security posture.
API security with agent-based solutions
Agent-based security is a cutting-edge approach to API protection, leveraging software agents deployed within an organization’s infrastructure to monitor, detect, and respond to security threats in real time. These agents interact directly with the APIs, analyzing incoming traffic and identifying potential vulnerabilities in API calls. They operate at the runtime level, ensuring that API requests are validated, authenticated, and authorized before any data is processed or exchanged.
This close proximity to API endpoints allows agent-based solutions to detect even subtle deviations from normal behavior, which could indicate emerging threats like denial-of-service (DoS) attacks or attempts to exploit unpatched vulnerabilities. By automating these security checks, organizations can reduce the risk of successful cyberattacks, especially within cloud native workloads.
Additionally, agent-based security offers significant advantages for cloud environments, where scalability and flexibility are critical. It can easily scale across distributed systems, offering consistent protection regardless of the size or complexity of the API landscape.
Benefits of agent-based API monitoring
Agent-based API security offers a range of benefits that make it an effective approach for securing APIs and protecting sensitive data. Here are some key advantages:
- Granular access control: By using agent-based API security, organizations can precisely regulate access, making sure that only authorized individuals or entities can use API resources. This reduces the likelihood of data breaches from unauthorized access.
- Real-time threat detection: Agent-based API security uses intelligent agents that continuously monitor incoming requests for any suspicious activities or patterns. These agents use machine learning algorithms or predefined rules to swiftly identify potential threats like brute-force attacks or abnormal behavior. The early detection provided by these agents enhances the organization’s ability to respond promptly and mitigate any harm caused by malicious actions.
- Proactive security measures: Rather than solely depending on reactive tactics such as firewalls or intrusion detection systems, agent-based API security adopts a proactive strategy to safeguard APIs. These agents actively evaluate every request in the moment and respond according to predetermined policies or changing circumstances. This proactive approach aids in detecting and resolving potential risks before they develop into major security breaches.
- Data protection through encryption: Agent-based API security enables safe interaction between clients and servers by utilizing widely accepted encryption methods, such as TLS/SSL, to safeguard sensitive information. This guarantees privacy during data transmission over networks and prevents unauthorized access or manipulation.
- Scalability and flexibility: Agent-based approaches are highly scalable because multiple intelligent agents can be deployed within the infrastructure to manage various aspects of API security concurrently, without causing performance degradation. Moreover, these agents can adapt to evolving threats by dynamically updating their rulesets, ending the need for major changes to the underlying infrastructure.
Addressing API vulnerabilities with agent-based approaches
One of the key strengths of agent-based security lies in its ability to pinpoint API vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. API vulnerabilities often arise from misconfigurations, exposed endpoints, or weak authentication mechanisms, making them prime attack vectors for cybercriminals. By continuously monitoring API traffic, agent-based solutions can detect anomalous behaviors, such as unusual traffic spikes or unauthorized attempts to access sensitive data.
For example, in distributed environments where microservices interact via APIs, an agent-based system can identify cross-service vulnerabilities and ensure that proper security policies are in place to protect against unauthorized access. The ability to monitor runtime behavior allows organizations to implement automated responses, such as throttling traffic or blocking malicious IP addresses, to mitigate risks in real time.
Moreover, agent-based security provides detailed auditing and logging capabilities, enabling security teams to perform thorough post-incident analysis. This ensures continuous improvement of security protocols and offers valuable insights for future cybersecurity strategies.
Agent-based vs. out-of-band API security
Agent-based API security and out-of-band API security are two distinct approaches to securing APIs, each with its own advantages and considerations. Let’s explore the key differences between these two methods:
Agent-based API security involves implementing intelligent software agents that act as intermediaries between clients and servers. These agents deeply understand the requests made to the API and can enforce security policies in real time.
Out-of-band API security involves implementing additional layers of protection beyond the regular flow of API operations. This approach places additional checks, such as web application firewalls (WAFs), intrusion detection systems (IDS), or other third-party tools, outside the core infrastructure environment where APIs operate. This isolation prevents direct impact on production environments.
Unlike agent-based approaches that require integration within the infrastructure, out-of-band solutions can be implemented independently of the APIs themselves. This simplifies the process of deploying and maintaining diverse sets of APIs.
Agent-based vs. agentless API security
When considering API security solutions, organizations often weigh the benefits of agent-based security against agentless approaches. Both have their merits, but they differ significantly in their operation and scope.
Agent-based security, as mentioned earlier, involves deploying software agents within the API’s runtime environment. These agents offer deep integration with the API ecosystem, providing precise control and real-time threat detection. The key benefit is their ability to secure API endpoints, monitor for vulnerabilities, and respond immediately to attacks.
On the other hand, agentless approaches rely on external monitoring tools, such as WAFs or cloud security platforms, that do not directly interact with the API’s runtime environment. While agentless solutions offer simplicity and ease of deployment, they may lack the granularity and real-time responsiveness provided by agent-based security. Additionally, agentless approaches can sometimes introduce latency, especially during complex API transactions, which could impact the overall performance of the system.
Ultimately, the choice between agent-based and agentless security depends on an organization’s specific requirements. For businesses seeking precise, automated protection that can scale across cloud native environments, agent-based solutions often provide a more comprehensive and proactive approach.
Frequently Asked Questions
Agent-based API security provides deep integration with the API ecosystem, enabling real-time threat detection, automated responses to security incidents, and precise control over API traffic. Agent-based solutions can quickly identify and mitigate vulnerabilities within the API’s runtime environment. In contrast, agentless solutions are easier to deploy but may lack the granular control and immediate responsiveness offered by agent-based approaches.
Agent-based security can detect unusual traffic patterns, such as an overwhelming number of requests from a single IP or distributed sources, which are characteristic of DoS and DDoS attacks. By monitoring API calls in real time, agents can identify these attacks early and automatically trigger countermeasures, such as rate limiting, blocking malicious IPs, or redirecting traffic to prevent service disruptions.
In cloud native applications and environments, agent-based solutions provide scalable and flexible security by embedding agents within distributed API workloads. These agents ensure consistent protection across cloud infrastructure, dynamically adjusting to the runtime behavior of microservices and applications. This approach is ideal for securing APIs in modern cloud-based architectures where scalability and agility are critical.
Agent-based solutions enhance API security by ensuring that only authorized and validated API calls are allowed. This guarantees the durability and integrity of API transactions while supporting interoperability across different services. The agents enforce security protocols such as encryption and authentication, making sure APIs can communicate securely and reliably, even in complex environments.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.