Shadow APIs often exist outside the standard security protocols, making them vulnerable to exploitation. Without real-time monitoring and discovery, they can expose sensitive data and provide entry points for attackers, thereby compromising the overall security of the application.
The phrase “shadow API” sounds mysterious, maybe even dangerous. In reality, shadow APIs are not the stuff of ghost stories or spy thrillers, but they can expose organizations to cyber risk and compliance problems. A shadow API is an application programming interface (API) that exists outside of normal controls and cyber defenses, similar to the idea of shadow IT. For this reason, they can be attractive targets for malicious actors. This article explores the nature of shadow APIs and what can be done to prevent them from causing harm.
To understand shadow APIs, it’s useful to contrast them with their conventional cousins. An API should be known to the IT department that deployed it. It ought to be registered with an API management tool, governed by policies, and protected by security controls. Call these “normal APIs.” In contrast, a shadow API comes into existence outside of regular view — under the radar, so to speak.
There isn’t anything sinister going with a shadow API. Developers create them all the time for good reasons and with the best of intentions. For example, a developer might need an API for a project and quickly throw one together for a purpose that is known to the dev team, but no one else. The API might serve as a connector between two applications that lack “out of the box” APIs. The team is in a rush, so there’s no time to subject the API to any official governance procedures. It remains invisible to API management and security tools. It is in the shadows.
A shadow API can also be an API developed by a third party, such as a software as a service (SaaS) vendor. It’s a regular API, in common use. However, if a team deploys it without including it in the organization’s API management system, it exists in the shadows. It’s out of sight and exposing the organization to risk.
Why are shadow APIs dangerous?
A shadow API represents a point of vulnerability. It probably lacks the right authentication and access controls. It might expose sensitive data to unauthorized users, or even the general public. Hackers can also use the shadow API to gather information about an organization and plan their attacks accordingly. And, what is particularly problematic is that all this vulnerability is occurring completely out of view from security monitoring solutions. By the time anyone notices a problem, such as data exfiltration, a shadow API attack is probably well under way. Data breaches and system outages caused by shadow APIs are costly to handle. They can also lead to problems with regulatory compliance, e.g., with consumer privacy laws.
Shadow APIs vs zombie APIs
For some people, a shadow API is indistinguishable from a “zombie API,” but they are not the same thing. While both are ungoverned, unsecured, and invisible, the zombie API was once a normal API. It just got forgotten or was abandoned. For instance, if the obsolete version of an API, which got replaced by a new edition a few months ago, is still running, it’s a zombie API. This is more common than one might imagine.
Zombie APIs present a range of security and compliance risks. They are not patched, for instance. Nor are they monitored for suspicious activity.
Why make the distinction? The reason to differentiate shadow APIs from zombie APIs has to do with avoiding the situation in the first place. A shadow API comes into existence because someone wants it to be in existence. A zombie API exists due to neglect of API governance policies. Each problem requires a different solution.
API gateways and shadow APIs
API gateways play a vital role in managing and securing the flow of API traffic between clients and services, acting as a centralized control point for API calls. However, when shadow APIs operate outside the purview of an API gateway, they bypass these essential security and traffic management controls. This lack of oversight is what makes shadow APIs particularly dangerous, as they are not subjected to the same authentication, rate limiting, and monitoring processes managed by the gateway.
By ensuring that all APIs, including shadow APIs, are properly registered with the API gateway, organizations can enforce standardized security protocols, such as encryption and authentication, while gaining visibility into all API traffic. API gateways also enable security teams to monitor usage in real time, flagging any anomalous or unauthorized API calls that could signal a security threat. Integrating shadow APIs into the API gateway not only helps in streamlining traffic management, but also reduces the risk of unmonitored APIs exposing the organization to cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
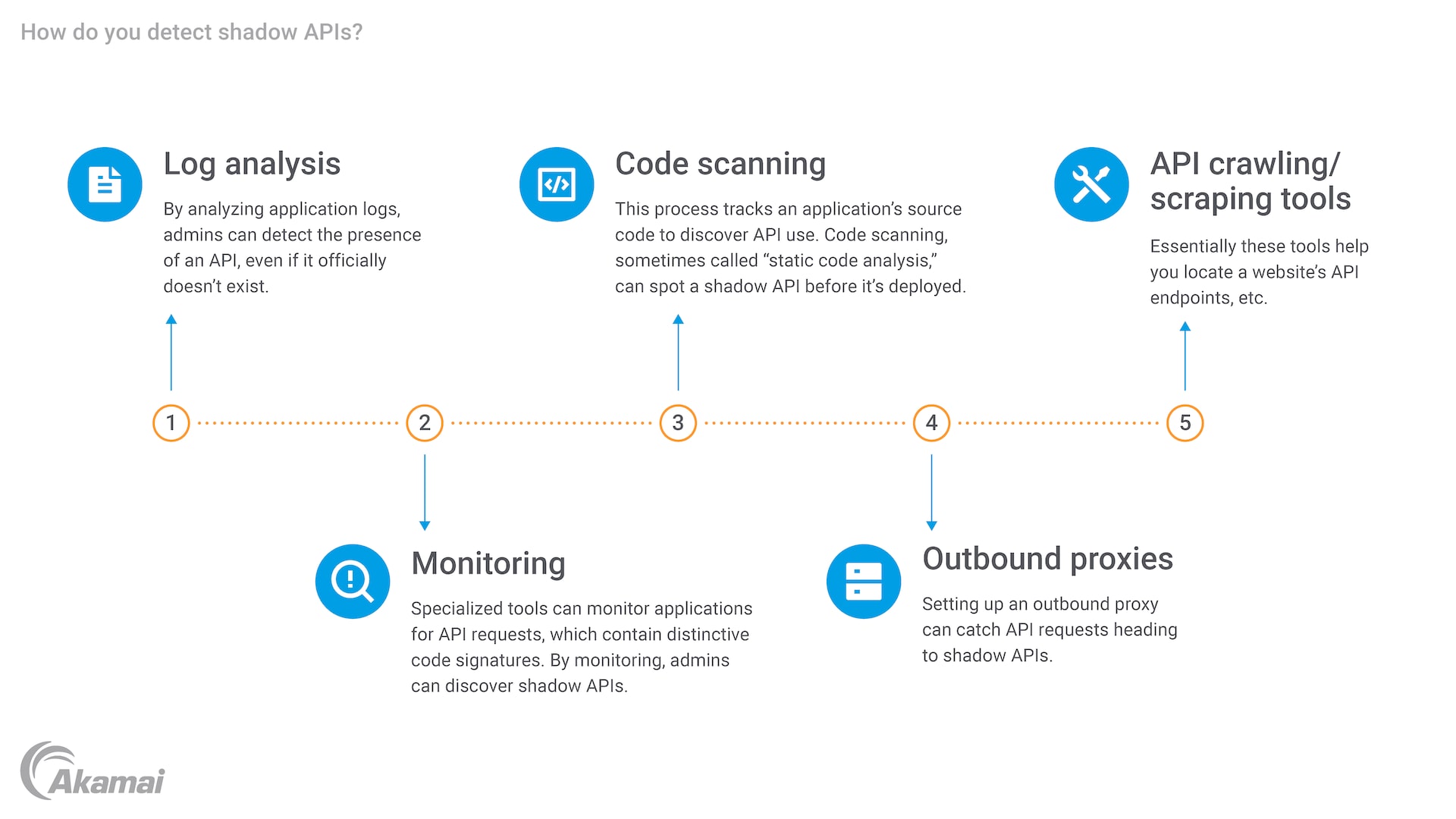
How to detect shadow APIs
Shadow APIs present a conundrum for API security managers. If they’re invisible, how does anyone even know to address their risk? The answer is that one should make an effort to discover them, so they will become visible. A number of techniques are effective at detecting shadow APIs. They include:
- Log analysis: By analyzing application logs, admins can detect the presence of an API, even if it officially doesn’t exist.
- Monitoring: Specialized tools can monitor applications for API requests, which contain distinctive code signatures. By monitoring, admins can discover shadow APIs.
- Code scanning: This process tracks an application’s source code to discover API use. Code scanning, sometimes called “static code analysis,” can spot a shadow API before it’s deployed.
- Outbound proxies: Setting up an outbound proxy can catch API requests heading to shadow APIs.
- API crawling/scraping tools: Essentially these tools help you locate a website’s API endpoints, etc.
Each of these techniques requires the organization to maintain a complete inventory of APIs to compare with the results of log analysis, monitoring, and so forth. Without such an inventory, no one would know if an API is supposed to be operating or not. An API management system is also necessary, because once the organization detects a shadow API, it needs a repeatable way to isolate it and apply controls to it — or take it down.
Real-time API monitoring to secure shadow APIs
In the context of shadow APIs, real-time API monitoring plays a crucial role in enhancing application security. Since shadow APIs often exist outside the awareness of security teams, they are not typically subject to regular security controls. By employing real-time monitoring, organizations can instantly detect suspicious API calls, including those originating from shadow APIs. This helps identify security vulnerabilities that may arise from unmonitored or undocumented APIs, giving security teams a chance to react quickly and mitigate potential threats before they escalate into full-blown cyberattacks.
Moreover, real-time API monitoring provides valuable insights into the behavior of both known and unknown APIs, offering a comprehensive view of the organization’s API landscape. This ensures that even shadow APIs, which were once hidden from security oversight, are brought into focus, reducing the overall risk of API vulnerabilities.
API discovery and audits for securing shadow APIs
Effective API discovery is a key strategy for detecting and managing shadow APIs, particularly in complex environments in which APIs are created and modified frequently. Through API discovery, organizations can map out their entire API ecosystem, identifying shadow APIs that may have been created without formal documentation or security controls. This discovery process is critical for security teams, as it uncovers gaps in application security that can be exploited by attackers.
Once shadow APIs are identified, it’s essential to conduct regular audits to assess their security posture. These audits help ensure that APIs, including shadow APIs, are not exposing sensitive data or allowing unauthorized access. By implementing API vulnerability assessments, security teams can uncover flaws such as insufficient authentication, misconfigurations, or outdated protocols that might be present in shadow APIs. This proactive approach helps maintain a high level of cybersecurity, even for APIs that initially flew under the radar.
Frequently Asked Questions
API discovery tools, along with real-time monitoring solutions, can help detect shadow APIs by scanning for undocumented API calls. Tools that analyze application logs, network traffic, and source code are effective in uncovering APIs and security risks that might otherwise be hidden.
Regular audits are crucial to identify security vulnerabilities in both known and shadow APIs. Audits help ensure that shadow APIs, once detected, are properly secured, governed, and monitored, thus reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Yes, once discovered, shadow APIs can be secured by bringing them under API management frameworks. Security teams can implement appropriate authentication, encryption, and access control measures, as well as integrate them into the organization’s real-time monitoring and auditing processes.
To minimize API vulnerabilities, including shadow APIs, security teams should work closely with development teams to implement continuous API security assessments during the software development lifecycle. Ensuring that all APIs are properly documented and subjected to vulnerability scans before deployment is essential.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai is the cybersecurity and cloud computing company that powers and protects business online. Our market-leading security solutions, superior threat intelligence, and global operations team provide defense in depth to safeguard enterprise data and applications everywhere. Akamai’s full-stack cloud computing solutions deliver performance and affordability on the world’s most distributed platform. Global enterprises trust Akamai to provide the industry-leading reliability, scale, and expertise they need to grow their business with confidence.